Describe How Plants Obtain and Use a Mineral Nutrients
This mode of nutrition in which plants take in nutrients from dead and decaying organic matter is called saprophytic nutrition. The combination of organic compounds along with water carbon dioxide and sunlight produce the energy that allows plants to grow.
Mineral Nutrition Study Guide Inspirit
Describe movement of xylem sap.
. Plants obtain water minerals and some oxygen from the soil. In the plant cell the nitrate ions are reduced to NH 2 group through series of enzymatic reactions. Plants obtain their inorganic nutrients from air water and soil.
Excepting the legumes plant obtains their nitrogen supply mainly in the form of nitrate NCT 3 from the soil but also as ammonium ions NH 4. Uptake assimilation and utilization of nutrients101102. A plant cannot use organic compounds such as those in manure or dead leaves until they are broken down into their elemental or ionic forms.
C percent of dry weight as inorganic minerals. Inorganic compounds form the majority of the soil solution. There are about 4100 species of parasitic plants.
Both the plants and animals require minerals essentially. Is this movement one-way only. Minerals are vital elements necessary for the body.
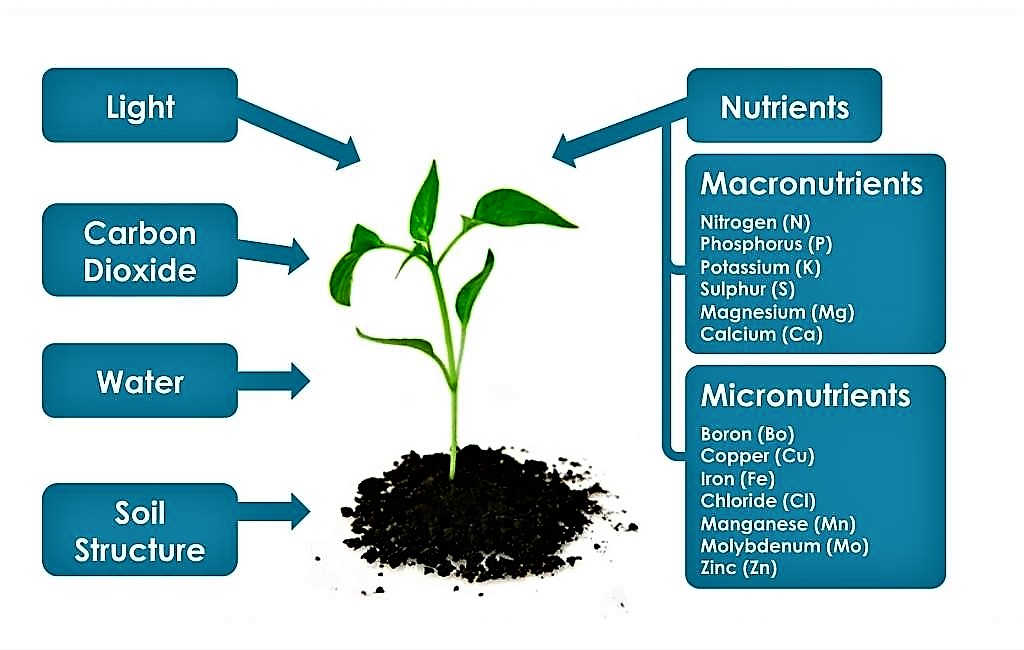
Mineral Nutrition is defined as the naturally occurring inorganic nutrient found in the soil and food that is essential for the proper functioning of animal and plant body. Need in relatively large amounts and micronutri-ents which plants need in small. What pulls xylem sap through the xylem cells.
Describe the chemical composition of plants including the. What is xylem sap. Just as people need calcium in their diets for strong teeth and bones plants need the mineral to build sturdy cell walls and healthy root systems.
Mass flow accounts for nutrient uptake of mobile nutrients such as nitrogen and sulfur. Scientists categorize the essential elements as macronutrients which plants. The mechanism that guides transport in the guard cells.
A percent of wet weight as water b percent of dry weight as organic substances and. The non-green plants called fungi derive their food from dead and decaying organic matter so fungi are saprophytes. The parasitic plant obtains water and nutrients through these connections.
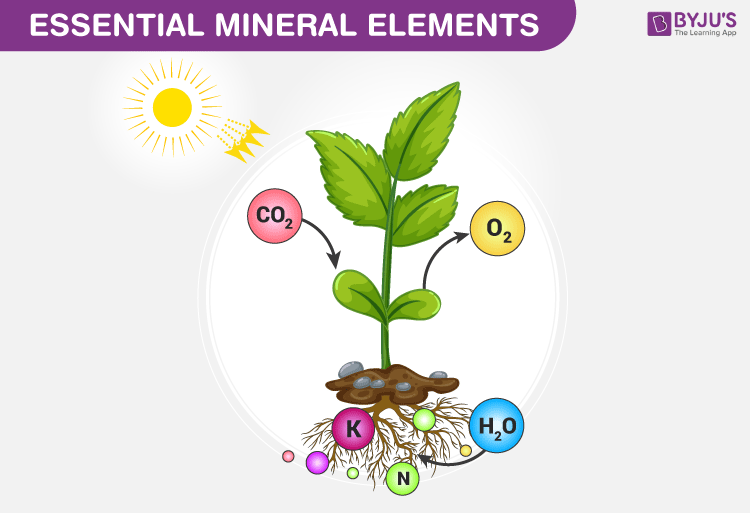
The plant is a total parasite a holoparasite because it is completely dependent on its host. Plants can absorb inorganic nutrients and water through their root system and carbon dioxide from the environment. Mineral nutrients A second plant structure point was earned for describing stomata as.
Root hairs that extend from the roots as a plant structure used in nutrient uptake. Some of the common fungi are mushroom bread mould and yeast. Where do plants obtain nutrients and water.
Record in your lab notebooks why you chose the location and describe how conditions are suitable for individual parts of the experiment. One point was earned for explaining that root hairs increase the surface area of the epidermis allow for more absorption of water. Nutrient use efficiency NUE shows the ability of crops to take up and utilize nutrients for maximum yields.
For example Zinc is necessary for the manufacture of protein. Plants growth uses air water and soil. The combination of organic compounds along with water carbon dioxide and sunlight produce the energy that allows plants to grow.
Develop a group schedule for plant cultivation daily watering responsibilities making and recording observations etc. They are absorbed through the roots by active transport as mineral ions dissolved in the soil water. Plants use nutrients from the air water and soil to make their own food through the process of.
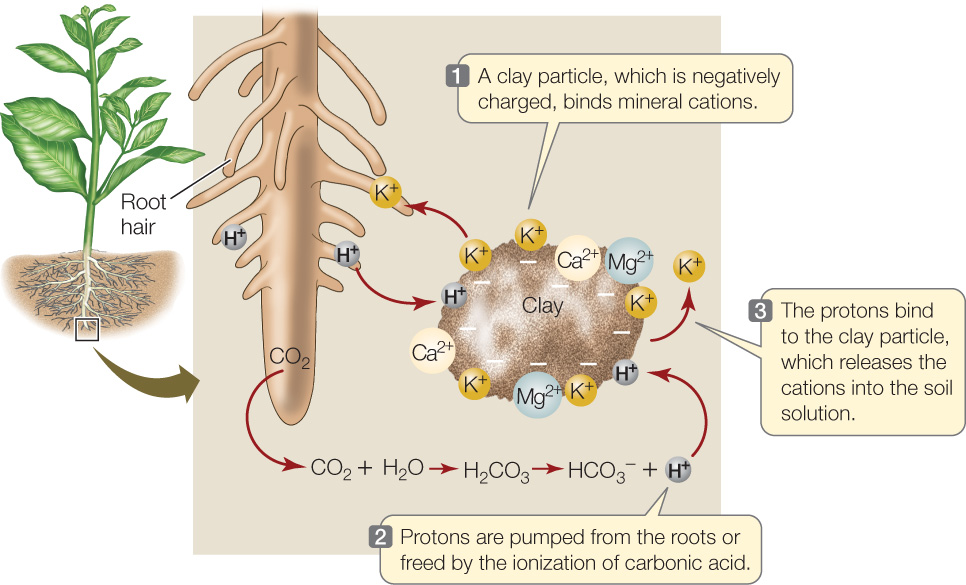
On the other hand variable charge minerals eg Fe oxides retain some nutrients P Zn by forming inner-sphere complexes Figure 2 and such nutrients are not readily available to plants. The nutrient must be in the form of either a positively charged ion cation or a negatively charged ion anion. Therefore the NUE concept involves three major processes in plants.
Legumes which possess Rhizobium bacteria in their nodules have the ability to utilize molecular nitrogen. More than 60 elements are found in plants but only 18 are considered essential elements see Table 1. Inorganic compounds form the majority of the soil solution.
These nutrients are essential for plant growth but they are needed in small or minute amounts. Hydrogen H As discussed in Chapter 9 Plant Growth and Development plants create their own food in the form of sugars through photosynthesis. Hemiparasites can photosynthesize but derive water and mineral nutrients from other plants exmistletoe holoparasites are completely parasitic and do not preform photosynthesisexwitchweed Compare the process in which ions and water are moved across the root cell plasma membrane vs.
Nutrientsboron chlorine copper iron manganese molybdenum nickel and zincare termed micronutrients. Plants need minerals for healthy growth. During diffusion roots grow throughout the profile and takes up nutrients.
What colors are these pigments. As the plant transpires water it draws water from the soil up through the root system. Calcium Ca Key functions.
Plants need an abundant supply of these three minerals which are common in most soils but must be provided via nutrient solution to hydroponic crops. Plants access water though the soil. How is sap movement aided.
Lab Questions How does the amount of available mineral nutrients affect plant growth. Calcium use efficiency CaUE which can be defined as shoot or grain yield per unit of Ca accumulated in. Leaving out a specific nutrient gives very specific symptoms.
Water is absorbed by the plant root transports nutrients throughout the plant and maintains the structure of the plant. Very exactly defined solutions will keep plants healthy. Other parasitic plants hemiparasites are fully photosynthetic and only use the host for water and minerals.
To be used by a plant an essential nutrient must be broken down into its basic form. Plants absorb minerals through roots by either passive or active processes.
Essential Mineral Elements In Plants Functions Types
13 Essential Plant Nutrients Micro And Macro Nutrients In Plants
Comments
Post a Comment